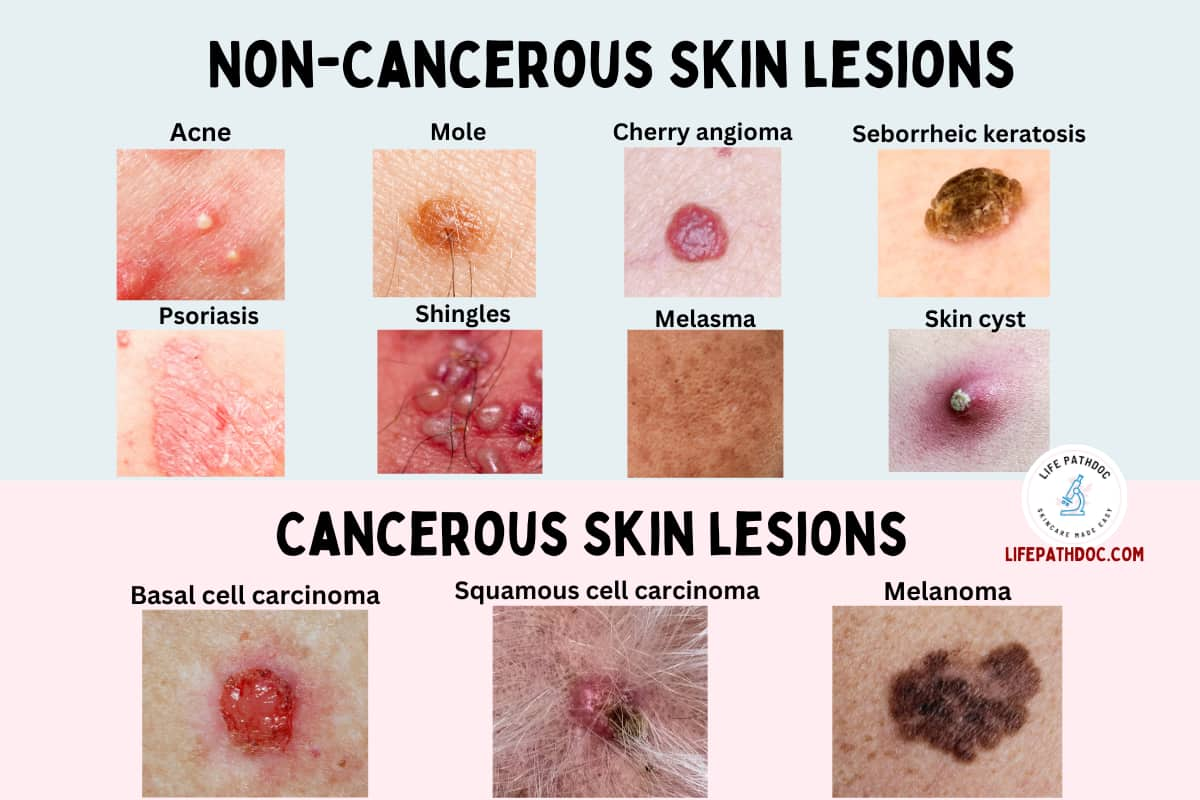
1. Acne

Acne is of two types: non-inflammatory and inflammatory.
- Non-inflammatory acne lesions include closed comedones and open comedones (blackheads).
- Inflammatory acne lesions include can present as papules, pustules, cysts, and nodules. Cysts and nodules appear when the inflammation goes deeper into the skin. They are often painful.
It is usually seen on the face, back, and chest.
Cause
The main causes behind acne are plugging of pores with oil and dead skin cells, inflammation, and proliferation of acne-causing bacteria. Hormones can drive sebum production in teenage years leading to acne.
Treatment
The treatment depends on the type and severity of acne. The ingredients used for treatment include – salicylic acid, azelaic acid, retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and antibiotics.
In severe cases, oral antibiotics and an oral form of vitamin A (Accutane) may be prescribed.
2. Actinic keratosis

Actinic keratosis usually presents as rough or crusty skin lesions on sun-exposed areas like the face, scalp, and neck. The color can vary – tan, pink, red, or brown.
Cause
It is a precancerous lesion that occurs due to DNA damage in the epidermal cells (usually due to sun exposure).
Treatment
It can be treated with topicals like 5- fluorouracil, imiquimod, ingenol mebutate, or diclofenac or procedures like laser, freezing, or local excision.
If left untreated, it can progress to squamous cell cancer in around 5-10% of cases.
3. Birthmarks
NEXT PAGE