Insect bites and stings can lead to itchy red bumps or papules on the skin. In some cases, the bumps may form vesicles.
Cause
These occur due to the skin’s reaction to the secretion of insects or their stings. The common offenders are fleas, bed bugs, mosquitos, ants, flies, and bee stings.
Treatment
They usually clear on their own and do not require treatment. Antihistamines may help in reducing itching.
17. Keloid

Keloid presents as raised skin lesions that are skin-colored, red, or purplish in color. They are soft and rubbery in consistency. They may be associated with itching.
These are commonly seen on the pre-sternal areas on the chest, upper back, shoulders, or cheeks.
Cause
The formation of keloids is triggered by any skin injury. They occur due to the formation of excess collagen during the healing process.
Certain factors increase the risk of keloid formation. These include darker skin tone, age under 30 years, and family history of keloids.
Treatment
They can be difficult to treat and may grow back. The treatment options include silicone or pressure dressing, steroid injections, laser, freezing, or surgical excision.
18. Keratosis pilaris

Keratosis pilaris can lead to tiny red raised skin lesions (papules) with rough surfaces that can feel like sandpaper. These usually appear on the cheeks, upper arms, thighs, or buttocks.
It is common in children and adolescents and clear by the age of 20-30s.
Cause
It is thought to occur due to blockage of the hair follicles with a protein called keratin. Keratin is part of the outer layer of our skin.
Genetics and atopic dermatitis may play some role in causing it, although the exact cause is not clear.
Treatment
It is harmless and goes away on its own. Some skincare ingredients may help in improving their appearance like retinoids, urea, lactic acid, or glycolic acid. Moisturizers can reduce the rough texture.
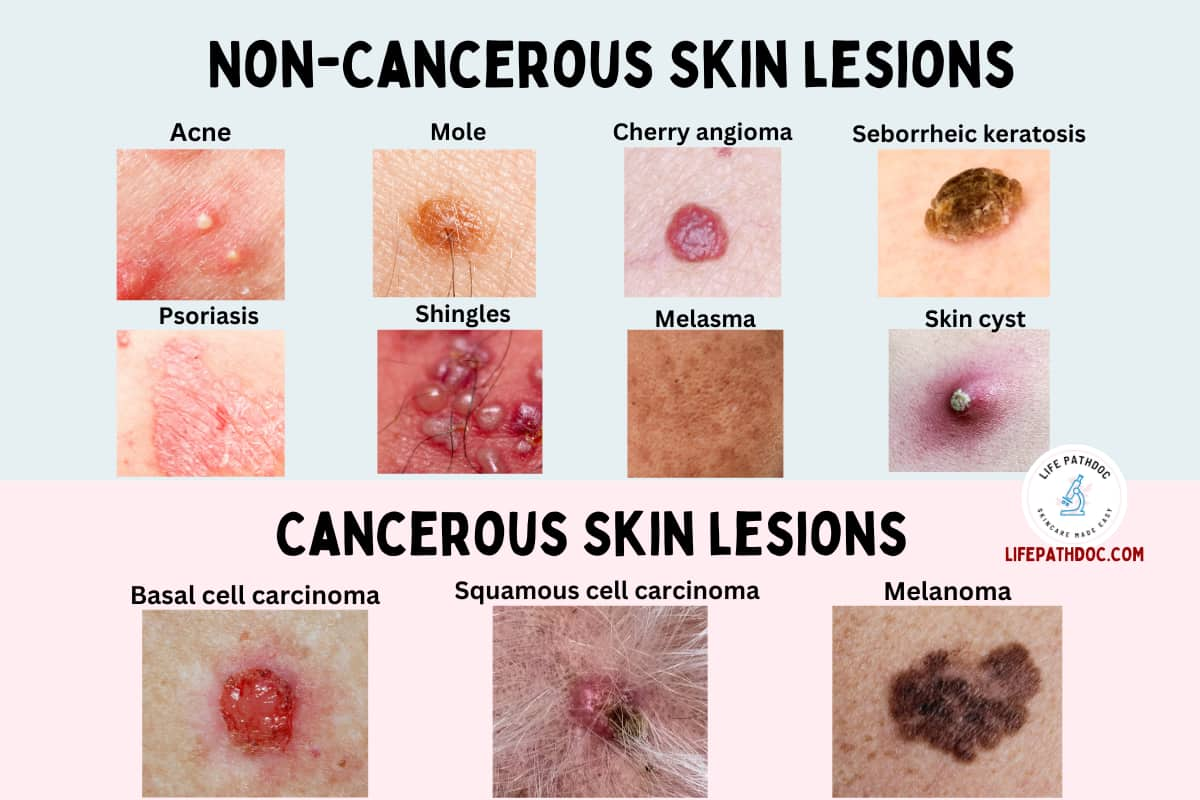
19. Melasma

Melasma is a common skin condition that leads to symmetrical flat dark patches on the face. They are usually located on the cheeks, nose, forehead, chin, and upper lip.
They can be any shade of brown, gray, or bluish in color. It often affects women between the ages of 20 and 40, especially during pregnancy.
Cause
Hormones and sun exposure are one of the main causes behind it. These can lead to the overproduction of melanin pigment leading to dark patches on the face.
Treatment
It is harmless but can be a cosmetic issue. It can be resistant to treatment.
The treatment options include topicals like hydroquinone, retinoids, kojic acid, arbutin, azelaic acid or niacinamide. In some cases, procedures like chemical peels and lasers may improve them. Adequate sun protection is important to treat and prevent them.
20. Milia
NEXT PAGE