Milia are small pearly white bumps or cysts that are commonly seen on the face (especially on the cheeks, nose, and under the eyes). They are often seen in infants but they can occur at any age.
Cause
These occur due to the trapping of dead skin cells under the skin. These cells can become hard resulting in these white cysts.
Several factors are associated with their formation:
- Damage to the skin barrier or skin injury.
- Sun exposure.
- Long-term use of steroids.
- Genetics.
- Autoimmune skin conditions.
- Heavy and occlusive cosmetics.
- Procedures like microdermabrasion and laser resurfacing.
Treatment
They are harmless and usually go away on their own in a few weeks or months. Topicals like salicylic acid and retinoids like retinol can help in clearing them.
If they don’t help, prescription-strength retinoids like tretinoin or procedures done in a doctor’s office like deroofing, freezing, chemical peels and laser ablation may resolve them.
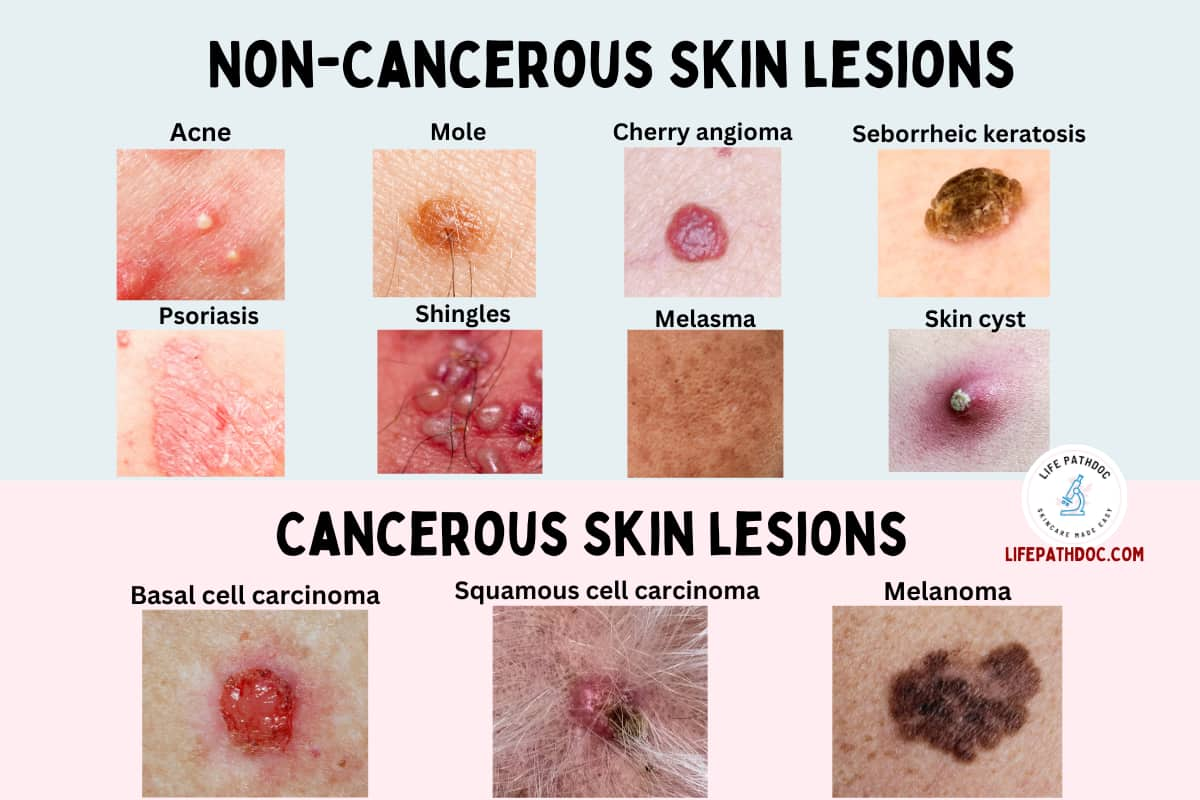
21. Moles

Moles are skin growths that consist of melanocytes, the cells that make melanin pigment and give color to our skin. They can be present at birth or can be acquired during a lifetime.
They present as round to oval flat or raised skin lesions – macules, papules, or nodules.
Treatment
They are usually harmless and do not require any treatment. If needed, your doctor can remove them by shaving or excision.
One should regularly examine moles for any suspicious changes in size, color, shape, or border. These may be signs of melanoma which is a type of skin cancer.
22. Psoriasis

Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition and is of various types. Plaque psoriasis is the most common type. It starts as red papules or bumps that come together to form red raised skin lesions – plaques.
They are covered with white or silvery scales. If the scales are removed, it leads to a pinpoint bleeding spot, this is called the Auspitz sign.
The commonly affected areas are elbows, knees, scalp, and trunk. One may also see changes in nails and joints.
Cause
The exact cause is not known. However, our immune system, genetics, and environmental factors may play a role in it.
Treatment
The treatment depends on the severity of the disease. It includes:
- Topicals containing coal tar or salicylic acid.
- Topical or oral steroids.
- Immunosuppressants.
- Vitamin D or A derivatives.
- Phototherapy.
23. Ringworm

Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection of the skin, hair, and nails. Depending on the part of the body involved it can have different names. The ringworm of the foot is called tinea pedis, ringworm of the hands is called tinea manuum, and ringworm of the body is called tinea corporis.
The symptoms may vary depending on the area involved. In general, the ringworm presents with a red circular rash that has a clear center giving it the appearance of a ring.
The periphery is raised and, in some cases, small red papules or blisters may be seen.
Cause
The group of fungi that cause ringworm are called dermatophytes. Ringworm can spread by direct contact with the lesions, infected animals, contaminated surfaces, or soil.
Treatment
Mild cases of ringworm of the skin may be treated with over-the-counter antifungal products. In severe cases and ringworm of the beard, scalp, and nails, prescription medications and oral antifungals may be prescribed.
24. Rosacea
NEXT PAGE